VISITING HOURS:
Week Days - 9 am to 8 pmSundays - Only Emergency Cases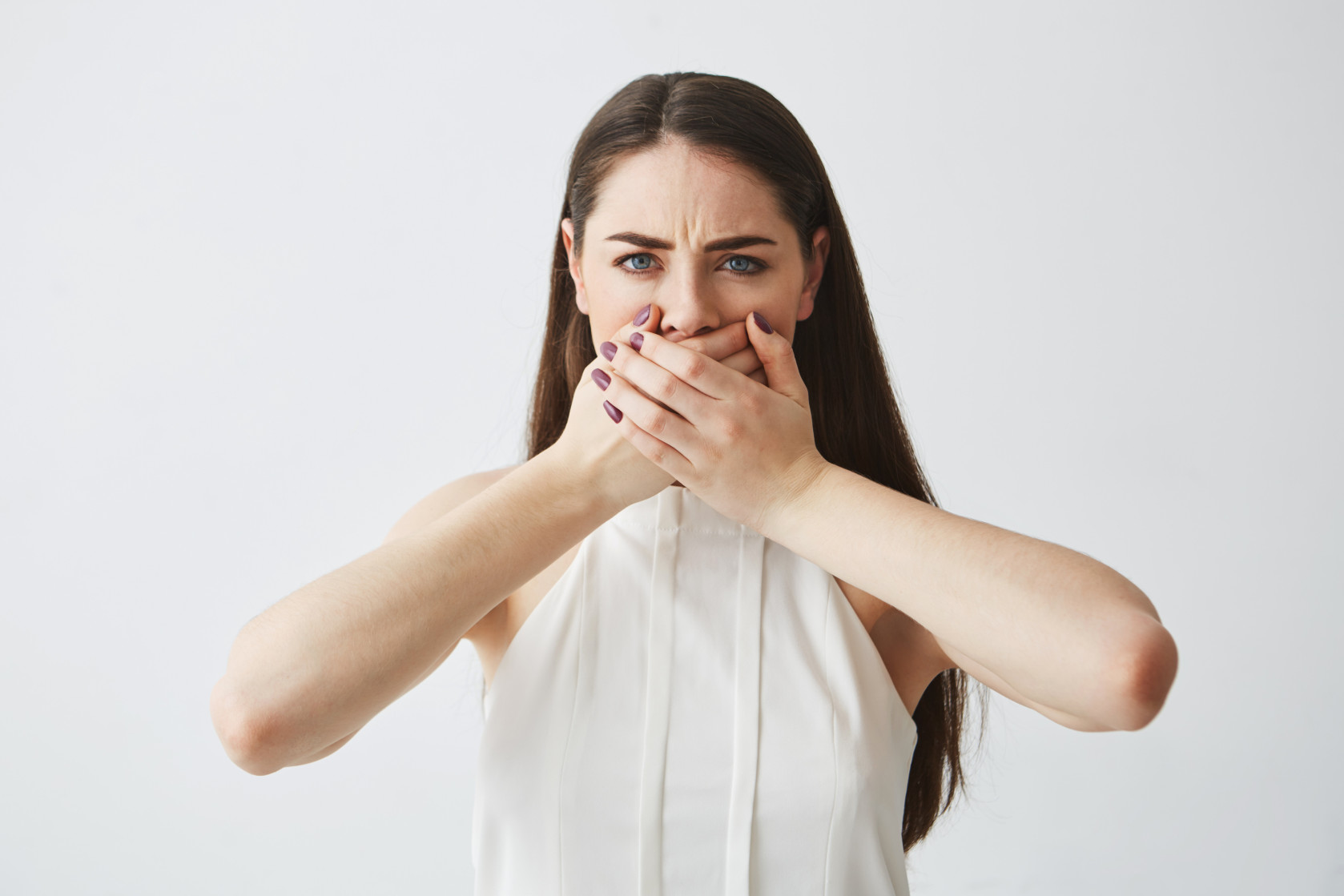
Dry Mouth and Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Dry mouth, symptomatically known as xerostomia, is one of the common indications linked with diabetes. It’s a complication associated with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes; however, not all diabetic patients experience it. It’s important to note that dryness of the mouth often accompanies non-diabetic conditions as well. If you notice persistent dryness and are experiencing issues with diabetes, it’s advisable to promptly consult your doctor. Learn more about dry mouth and diabetes and how they are connected.
Symptoms of Dry Mouth
At Dentique, we provide excellent care to help lessen the problems diabetes can cause for your oral health. Dry mouth is characterized by a decreased production of saliva, leading to various symptoms such as:
Rough, Dry Tongue: Moisture is essential for the smooth texture of the tongue; failure to supply it results in a rough and dry feeling.
Lack of Moisture in the Mouth: A dry mouth is a condition manifested in insufficient wetness in the mouth.
Frequent Pain in the Mouth: A dry mouth can cause repeated discomfort and pain in a person’s mouth.
Cracked and Chapped Lips: Cracked, and chapped lips are common symptoms when the mouth is dry.
Sores in the Mouth: Sore spots can develop in the mouth and the throat due to this situation which is highly uncomfortable.
Infections in the Oral Cavity: Dry mouth can create an environment conducive to oral infections.
Difficulty with Swallowing, Talking, or Chewing: Reduced saliva production can make activities like swallowing, talking, or chewing more challenging.
How Diabetes Causes Dry Mouth?
There is a link between dry mouth and diabetes, increased high blood sugar levels, or hyperglycemia, is one of the most common causes of dry mouth in people with diabetes. High glucose levels can cause the symptoms of dry mouth, although healthcare providers aren’t quite sure why. Another reason is that diabetes can damage the nerves that control the salivary glands that keep your mouth moist. Damage to these nerves can cause reduced saliva production, leading to dry mouth. Dry mouth can lead to complications such as gingivitis over the long term if left untreated.
Treatment of Dry Mouth Caused By Diabetes
The primary approach to dry mouth and diabetes treatment is addressing the underlying cause. If high blood sugar is the culprit, working with your healthcare provider to monitor and manage blood sugar levels is crucial. Adjustments to medications, including potential changes or lower doses, may be considered. Saliva substitutes, such as sorbitol, can also be recommended by healthcare providers. Dentists may recommend fluoride applications or gels to protect teeth from increased susceptibility to decay due to decreased saliva.
Preventing Dry Mouth in Diabetes

Prevention is key in managing dry mouth related to diabetes. Collaborating with the healthcare team, keep blood sugar within the target range. Effective diabetes management includes adopting a healthy, balanced diet, attending medical appointments, checking blood glucose levels, taking prescribed medications, engaging in regular physical exercise, and ensuring a healthy weight.
Home Remedies
To alleviate the symptoms of dry mouth at home, consider the following strategies:
Use lip balm to moisturize.
Boost saliva production by chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free hard candy.
Use a humidifier while sleeping at night.
Lifestyle Changes
The link between dry mouth and diabetes is well recognized. To prevent dry mouth, consider implementing these lifestyle changes:
Abstain from alcohol, tobacco, coffee, and sugary products or those with artificial sweeteners.
The best practice in good oral hygiene involves brushing your teeth and gums two times every day using fluoride toothpaste.
Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water daily.
Floss between teeth daily.
Limit consumption of salty and spicy foods.
Go to a dentist regularly, at least once, or a few times per year.
If you are looking for the best dental clinic in Kochi, book an appointment with Dentique now .
Other Reasons that Can Cause Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Dry mouth, usually known as xerostomia, could be due to several reasons other than high blood sugar. Some common causes include:
Nerve Damage: Damage to the nerves controlling salivary glands can lead to a dry mouth.
Dehydration: Dryness in the mouth can at times arise due to insufficient hydration.
Kidney Disease and Dialysis: Dryness in the mouth can affect persons on dialysis treatment because of kidney disease.
Mouth Breathing: Habitual breathing through the mouth can be a contributing factor.
Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like HIV, AIDS, and Sjögren’s syndrome are associated with dry mouth.
Smoking: Smoking tobacco can contribute to the development of dry mouth.
Medications: Some medications, including those for cancer, high blood pressure, depression, and bladder problems, may cause dry mouth.
Stress: Stress can impact salivary flow, leading to a dry mouth sensation.
Also Read: How Smoking Affects Your Teeth?
Understanding these various causes is essential for addressing and managing dry mouth effectively. If you’re experiencing persistent dry mouth, consulting with a professional dentist and getting expert dental treatment can help identify the specific cause and determine the most appropriate course of action.
When Do You Need to Visit Your Physician for Dry Mouth?
Dry mouth may be a symptom of onset diabetes. Ensure you raise it in your next visit to the healthcare provider. However, if you have diabetes and notice any of the following symptoms, it’s advisable to schedule an appointment sooner:
Bleeding from Your Teeth or Mouth: If you observe bleeding, it’s crucial to address this issue promptly.
Loose Teeth: Loose teeth can be indicative of oral health concerns and should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
Mouth Pain: Persistent pain in the mouth should not be ignored and warrants a timely discussion with your healthcare professional.
Sores in Your Mouth: The presence of sores in the mouth may require attention and investigation.
Trouble Chewing, Swallowing, or Talking: Difficulty with basic oral functions such as chewing, swallowing, or talking should prompt an earlier appointment for a thorough evaluation.
Being proactive about discussing these symptoms with your healthcare provider allows for timely intervention and management, ensuring comprehensive care for both your oral health and potential diabetes-related concerns.
Conclusion
Dry mouth is a prevalent symptom among individuals with diabetes, particularly those experiencing high blood sugar levels. Prolonged dry mouth in diabetes can lead to health issues, including the risk of gum disease and infections. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene practices is equally important to mitigate the potential complications associated with dry mouth in the context of diabetes. Regular check-ups and proactive dental care can contribute to overall oral health and help prevent further complications. Seeking advice from an experienced dentist and consulting with a doctor about your symptoms is crucial for proper assessment and management. Contact Dentique today for professional guidance and personalized care tailored to your needs.
OUR
TREATMENTS
TREATMENTS